Our Help Line
+91-987-114-2425
Contact Us
Quick Links
Know Your B.M.I.
Weight loss surgery procedures
1- Restrictive Procedures:
Decrease in food intake by creating a small upper stomach pouch or sleeve to limit food intake.- Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding (LAGB)
- Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy (LSG)
2- Mal- Absorptive Procedure:
Decrease in food intake by creating a small pouch of stomach by staples. In addition to this, initial segment of small intestine is By- passed, which facilitates reduced calories and nutrients absorption.- Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass (LGB)
Who needs Bariatric or weight loss surgery?
- BMI is >37.5 without co-morbidities.
- BMI is between 32.5 - 37.5 with serious weight related problems such as type 2 Diabetes, High blood pressure, Arthritis or Sleep apnea.
- In some special cases, you may qualify for certain types of weight loss surgeries if BMI is 30 and above and you have serious co-morbid health problems.
- All other methods of weight loss (exercise, dietary, medicines etc.) have failed to deliver a lasting solution.
- Unable to do routine activities due to severe obesity.
- Patients who have understood the surgical procedures for weight loss, the risks and after-effects of surgery and have consented for the same.

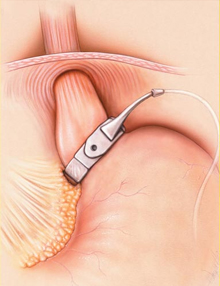
Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding (LAGB)
In this procedure a silicon band lined with an inflatable balloon is placed laparoscopically around the stomach near its upper end creating a small pouch (15 to 30 cc vol.) and a narrow passage leads into the larger remainder of stomach.
When a patient eats, the feeling of satiety or fullness of stomach is experienced early and therefore food consumption is reduced, leading to significant weight loss.
This balloon is connected to a small reservoir that is placed under the skin of the abdomen through which the diameter of the band can be adjusted by injecting fluid into it as an outpatient procedure.
- Performed laparoscopically with 5 small incisions ( less than 5 mm and one of 15 mm size).
- Adjustable 'silastic' gastric band used.
- Operative time approximately one hour.
- Short hospital stay of 1 to 2 days.
- Liquids can be taken orally from 1'st post-operative day.
- Quick recovery: back to work in one week.
- Resumption of strenuous activity in 2 weeks.
- Eliminates feeling of being always hungry.
- Food is absorbed normally.
- No vitamin and protein deficiency.
- No cutting or stapling of the stomach.
- Adjustable without additional surgery.
- Fully reversible: stomach returns to normal size if the band is removed.
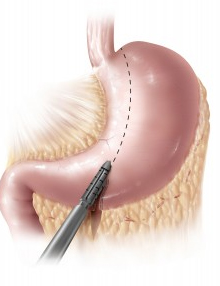
Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy (LSG)
Sleeve Gastrectomy is a technique that offers the same results as the Gastric Bypass but with less risk.
The Gastric 'Sleeve' is a new procedure that induces weight loss by restricting food intake (a restrictive procedure).
With this procedure, the surgeon removes approximately 80 percent of the stomach laparoscopically and with the help of staplers so that the stomach takes the shape of a tube or 'sleeve', or a very slim banana which measures from 30 to 50 cc depending upon the surgeon performing the procedure.
In addition to being restrictive, this procedure has seen that the hormone that regulates the appetite, the Ghrelina, diminishes, causing the patient to have less desire to eat.
- Performed laparoscopically with 5 small incisions (most less than 5 mm, two of 12 mm).
- Endostapler used to divide stomach.
- Takes about 1 to 2 hours to complete.
- Stay in hospital for 2 -3 days.
- Liquid diet for 2 weeks after the operation.
- Return to work in 1 to 2 weeks.
- Resume strenuous activity in one month.
- It is performed laparoscopically.
- It does not require disconnecting or reconnecting the intestines, as in bypass.
- No implant and adjustment required as in band surgery.
- Food is absorbed normally.
- No vitamin and protein deficiency.
- It is a technically simpler operation than the gastric bypass.
- Weight loss surgery of choice for high risk patients, especially those with anaemia, severe asthma, for patients on steroids, inflammatory bowel disease.
- Remaining stomach may stretch out.
- May require follow-up weight loss surgery for the morbidly obese.
- Not reversible.
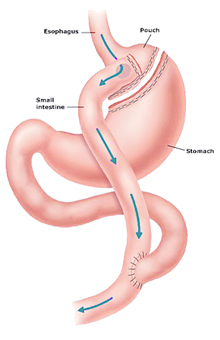
Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass
In a laparoscopic gastric bypass, the stomach is made smaller by creating a small pouch (30 ml) at the top of the stomach using surgical staples. The smaller stomach is connected directly to the middle porting of the small intestine (Jejunum), bypassing the rest of the stomach and the upper portion of the small intestine (Duodenum). The small stomach makes you feel full more quickly and part of small intestine bypass causes reduced calories and nutrient absorption, which ultimately leads to weight loss.
- Performed laparoscopically by 5-6 small 5 mm incisions, one of 15 mm.
- Hospital stay is required for 3-5 days.
- Liquid diet for two weeks after the operation.
- Return to work in 1-2 weeks.
- Normal activities in 1 month.
- Eliminates feeling of being always hungry.
- You eat small amount of normal food.
- Diabetes and other co-morbidities are usually resolved early.
- Sustainable long term weight control.
- This operation is more risky than the band or the sleeve gastrectomy
- Usually not reversible.
- Long term diet supplementation with vitamins and minerals is required.
Check-list before surgery
The thorough medical check by medical and surgical team to decide the type of surgery and assess your readiness for the operation and to rule out the following conditions, is required:- Endocrine related causes of obesity.
- Severe or uncontrolled psychological and mental illness.
- Alcohol or drug abuse.
Benefits of Bariatric Surgery
The medical and emotional benefits of weight loss procedures begin almost after surgery:- Significant weight loss
- Improvement of Type Ⅱ Diabetes
- Lower blood pressure
- Lower cholesterol
- Relief in sleep apnea
- Relief in acid reflux
- Decreased joint pain, improved mobility
- Improved mood and self-esteem
Risks of weight loss surgery
Weight loss surgery, as with any major surgery, has some associated risks of which you should be made aware of, these may include:- Leakage of digestive juice into the body cavity.
- Wound infection at incision sites.
- Hernias-a weakening of abdominal wall.
- Development of gall stones-due to rapid weight loss.
- Blood clots-may cause a more serious condition called a pulmonary embolism
- Vitamin deficiencies-may be preventable by taking daily vitamin supplements.
Life after Bariatric Surgery
After surgery there are three phases through which your diet progression will take place:| Stage-Ⅰ | Liquid diet | 1-15 Days |
| Stage-Ⅱ | Semi-solid diet | 15-30 Days |
| Stage-Ⅲ | Low fat solid diet | After 4 weeks of surgery |
- Medications for your co-morbidities i.e.diabetes, hypertension may need adjustment in consultation with your doctor.
- Lifestyle adjustment.
- Patient must learn to eat food in small amounts and to chew it well and slowly.
- Follow-up is necessary every month for 3 month after surgery and then as advised by your surgeon for dietary/nutritional counseling, for best results.
- Weight loss starts soon after surgery and continues for one and half to two years.
- Obesity surgery is not a cosmetic surgery. It leads to improved stamina, mood and self esteem with significant weight reduction.

